Sensitivity, Pain, Pimples, Abscesses, Facial Swellings, Broken Fillings, or Filling Fell Out etc?
Sensitivity to hot or cold
Pain on biting
Constant Pain
Fistulas (pimples)
Abscesses
Cellulitis (face swollen full of pus) - can be caused by tooth decay,
or impacted wisdom teeth etc.
Broken tooth
Broken fillings/crown, or filling/crown fell out
Broken dentures/prostheses
etc etc.
Please contact us on 3715 8885.
We will endeavour to fit you in as soon as possible, to primarly relieve you from pain, and to secondarily restore function and aesthetics.
 5.JPG)
Here is a fistula (or pimple) as pus tries to drain.
Sub-luxation (tooth knocked)
Sub-luxation is where the tooth has been hit.
The tooth is not loose.
The tooth has not been dislodged or knocked out either.
However, there may be bleeding emminating from the gums.
It may not heal properly by itself.
The tooth will have to be radiographed to check for signs of undetected root fracture, and even alveolar bone fractures.
The blood vessels and nerves supplying the tooth, may be crushed or severed.
Please contact us, as soon as possible.
Luxation (loose tooth)
If trauma causes teeth to become loose, then temporarily hold the tooth/teeth in position, and contact a dentist or doctor as soon as possible.
The loose tooth may need to be "fixed" by splinting.
Avulsion (tooth knocked out)
If trauma causes the tooth to be knocked out:
1. Baby teeth?
Baby teeth are normally left out, and NOT re-implanted.
2. Permanent teeth?
A. If possible, handle the tooth by the crown only, (do not touch the root/s), and try to gently push the tooth back into the socket, and hold it in position until you see a dentist.
B. If it is not possible to push the tooth back into the socket?
i. Handle the dislodged tooth by the crown only - do NOT touch the root of the tooth.
ii. Do NOT wash the tooth under tap water.
iii. Place the dislodged tooth in a small glass of milk - the tooth should NEVER be allowed to dry out.
iv. If a glass of milk is not possible, then:
a. Place the tooth in plastic wrap.
b. Or place the tooth in the patient's mouth, in the space between the lower cheek and the lower back teeth.
v. Contact a dentist immediately, or if not possible, contact a medical doctor.
Managememt of Trauma
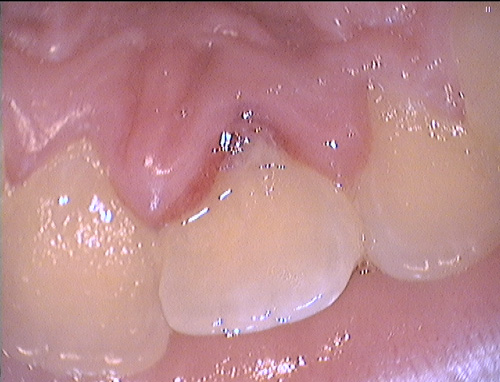
Here is an example of the management of trauma at Mt Ommaney Dental.
This boy encountered trauma in the playground.
The tooth has been pushed in.
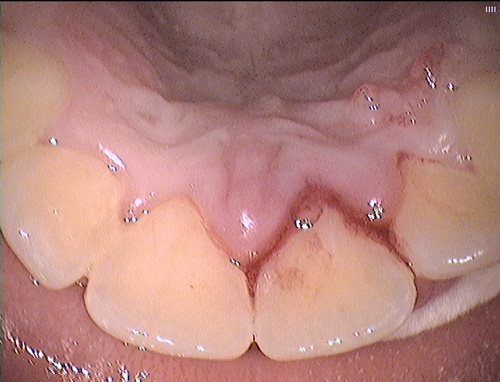
Under anaesthetic, the tooth has now been repositioned to the original state.
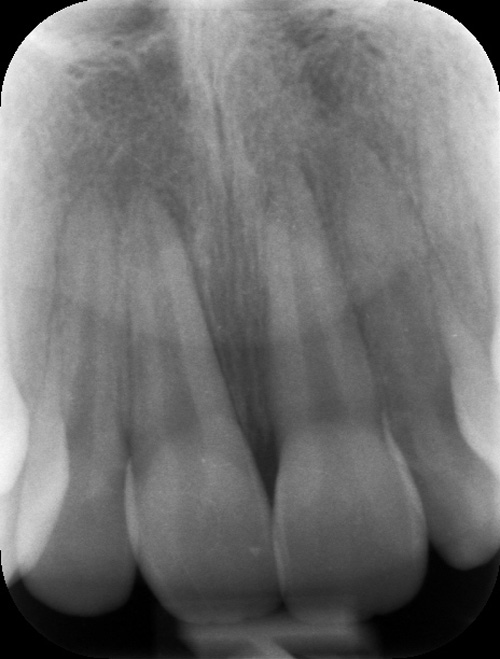
X-ray showing the tooth pushed in, looking front on.
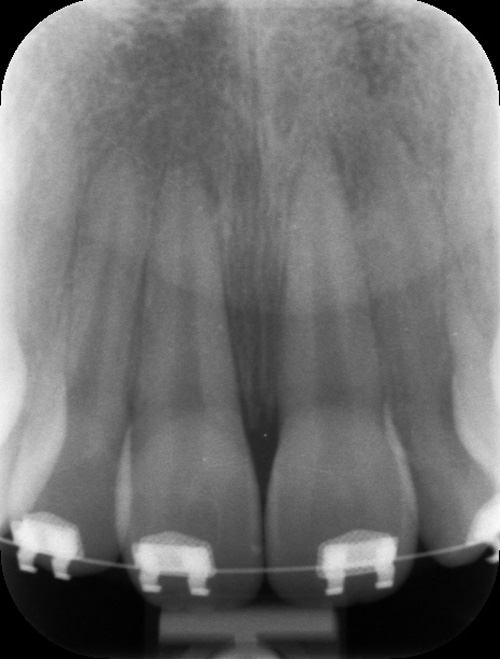
X-ray showing the tooth repositioned to it's original state with temporary light wire fixation under anaesthetic.
The physical trauma often damages the nerves and blood vessels inside the root canal.
This internal bleeding may cause the tooth to become darker immediately, or at a later date.
In time, this can lead to the death of the tooth, so that root canal treatment may be required to prevent abscess formation and severe pain. |